Turning the Tide on Opioid Prescribing Practices
In 2017 there was a continued increase in opioid-related deaths in the United States, with more than 60,000 lives lost. Most opioid abusers report that their opioids are acquired with their own prescription or a prescription for someone else obtained illegally. Two recent retrospective studies found that in patients undergoing surgery for early non–small cell lung cancer, perioperative opioid use was associated with decreased OS and increased risk of recurrence.

Patrick I. Borgen, MD, is the chairman of the Department of Surgery at Maimonides Medical Center and director of the Brooklyn Breast Cancer Program in Brooklyn, New York. Kristin Rojas, MD, is an obstetrician-gynecologist affiliated with Maimonides Medical Center in the Brooklyn, New York, and Parkland Health & Hospital System in Dallas, Texas.
In 2017 there was a continued increase in opioid-related deaths in the United States, with more than 60,000 lives lost.1Most opioid abusers report that their opioids are acquired with their own prescription or a prescription for someone else obtained illegally.2The majority of the abused opioids are diverted from physician prescriptions, and physicians find themselves at a critical junction that will determine the course of this lethal epidemic.3
In addition to their addictive potential, opioids have untoward effects that are less well known. They impair immune responses, increase angiogenesis, and affect the function of natural killer cells and T cells.4Opioids may also directly act on tumor cells to encourage growth and metastasis.5Gupta and her colleagues demonstrated that tumor volume and vascularization of implanted breast cancer were significantly increased in an opioid-treated mouse model, compared with a control cohort treated with naloxone, a mu opioid receptor (MOR) and nonselective receptor antagonist. These effects are thought to be attributable to the direct stimulation of the MOR or its interaction with the VEGF receptor.6,7
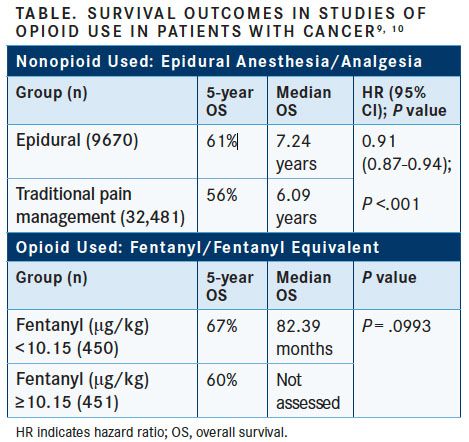
The tumorigenic effect of opioids has been further investigated in human studies. A study of a large cohort of 42,151 patients undergoing surgery for colon cancer found that the oncologic outcomes of those who received systemic opioid analgesia were inferior to those of patients who received epidural anesthesia. The nonopioid group had significantly longer overall survival (OS), although the cancer recurrence rates were similar.8Two recent retrospective studies found that in patients undergoing surgery for early nonsmall cell lung cancer, perioperative opioid use was associated with decreased OS and increased risk of recurrence (TABLE).9,10Pooled data from 2 randomized placebo-controlled trials found that in patients with end-stage cancer and opioid-induced constipation, those treated with methylnaltrexone (MOR antagonist) had a longer median OS, and response to therapy was found to be an independent prognostic factor. Of note, no improvement in OS was observed among the 134 patients with advanced illness treated with methylnaltrexone versus placebo, suggesting that the beneficial effects on survival are oncology related.11These lines of evidence in both mouse and human models suggest a correlation between activation of the MOR and worse oncologic outcomes.
But uncontrolled pain, specifically around the time of the homeostatic disruption of a cancer operation, may also promote inferior oncologic outcomes. Endorphins can bind to the MOR in a dose-dependent fashion, and the catecholamines associated with pain and the perioperative stress response may directly affect either postexcision residual tumor cells or occult distant metastases.12The argument to eliminate opioids should focus on adequate pain control without opioids rather than simply eliminating the use of opioids.
In the 1990s there was a surge in the use of opioids after regulatory agencies, including the Joint Commission, aggressively promoted assessing and treating pain, called the “fifth vital sign.”13-15Drug manufacturers were accused of downplaying the dangers of opioid addiction in order to boost highly lucrative sales.16This “destigmatization” of this drug class, along with public deception regarding their safety, led to the widespread liberalization of opioid prescriptions.
The evolving conceptualization of the management of surgical pain has been a major contributor to the supply of narcotics that led to the opioid crisis. Recently, healthcare providers have sought to develop and implement opioid-minimizing perioperative protocols to minimize the dispensing of superfluous opioids available for diversion within their communities.
Our group of surgeons in a large Brooklyn, New York, hospital has implemented a multimodal analgesia plan for all patients with breast cancer undergoing lumpectomy and mastectomy without reconstruction. Lax opioid-dispensing policies were broken down and rebuilt from the ground up, and our experience was recently published. Since the postoperative protocol’s inception, more than 300 lumpectomy patients have been discharged without a single narcotic prescription.17As the protocol was further expanded to mastectomy without reconstruction, postoperative pain scores and complication rates have remained low.
By implementing protocols employing multimodal analgesia and opioid-sparing techniques, the face of surgical oncology care will continue to evolve. As evidence grows that opioids may potentially worsen oncologic outcomes, surgeons and oncology providers must take an active role in addressing the opioid crisis by adopting similar protocols that decrease the quantity of narcotics available for diversion while ensuring safe patient care. We have an obligation to change practice patterns in our own clinics, hospital hallways, and operating rooms, ignoring the impulse to distribute superfluous narcotics for every surgical procedure.
References:
- Overdose death rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse website. drugabuse.gov/related-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates. Updated August 2018. Accessed September 26, 2018.
- Jones CM, Paulozzi LJ, Mack KA. Sources of prescription opioid pain relievers by frequency of past-year nonmedical use: United States, 2008-2011.JAMA Intern Med.2014;174(5):802-803. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12809.
- Shei A, Rice JB, Kirson NY, et al. Sources of prescription opioids among diagnosed opioid abusers.Curr Med Res Opin.2015;31(4):779-784. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1016607.
- Liang X, Liu R, Chen C, Ji F, Li T. Opioid system modulates the immune function: a review.Transl Perioper Pain Med.2016;1(1):5-13. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/ PMC4790459/
- Afsharimani B, Cabot P, Parat MO. Morphine and tumor growth metastasis.Cancer Metastasis Rev.2011;30(2):225-238. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9285-0.
- Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Chang L, et al. Morphine stimulates angiogenesis by activating proangiogenic and survival-promoting signaling and promotes breast tumor growth.Cancer Res.2002;62(15):4491-4498. cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/62/15/4491.
- Nestler EJ, Hyman SE, Holtzman DM, Malenka RC.Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience.3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education/ Medical; 2015.
- Cummings KC 3rd, Xu F, Cummings LC, Cooper GS. A comparison of epidural analgesia and traditional pain management effects on survival and cancer recurrence after colectomy: a population-based study.Anesthesiology. 2012;116(4):797-806. doi: 10.1097/ ALN.0b013e31824674f6.
- Cata JP, Keerty V, Keerty D, et al. A retrospective analysis of the effect of intraoperative opioid dose on cancer recurrence after non-small cell lung cancer resection.Cancer Med.2014;3(4):900-908. doi: 10.1002/cam4.236.
- Maher DP, Wong W, White PF, et al. Association of increased postoperative opioid administration with non-small cell lung cancer recurrence: a retrospective analysis.Br J Anaesth.2014;113(Suppl. 1):i88-i94. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu192.
- Janku F, Johnson LK, Karp DD, Atkins JT, Singleton PA, Moss J. Treatment with methylnaltrexone is associated with increased survival in patients with advanced cancer.Ann Oncol.2018;29(4):1076. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx776.
- Chakroborty D, Sarkar C, Basu B, Dasgupta PS, Basu S. Catecholamines regulate tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Res.2009;69(9):3727-3730. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4289.
- Volkow ND, McLellan AT. Opioid abuse in chronic pain--misconceptions and mitigation strategies.N Engl J Med.2016;374(13):1253-1263. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1507771.
- Phillips DM. JCAHO pain management standards are unveiled. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations.JAMA.2000;284(4): 428-429. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.4.423b.
- Kozol RA, Voytovich A. Misinterpretation of the fifth vital sign.Arch Surg.2007;142(5):417-420. doi: 10.1001.archsurg.142.5.417.
- Keefe PR. The family that built an empire of pain. The New Yorker. newyorker.com/magazine/2017/10/30/the-family-that-built-an-empire-of-pain. Published October 30, 2017. Accessed October 22, 2018.
- Rojas KE, Manasseh DM, Flom PL, et al. A pilot study of a breast surgery Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol to eliminate narcotic prescription at discharge.Breast Cancer Res Treat.2018;171(3):621-626. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4859-y.

Gasparetto Explains Rationale for Quadruplet Front Line in Transplant-Ineligible Myeloma
February 22nd 2025In a Community Case Forum in partnership with the North Carolina Oncology Association, Cristina Gasparetto, MD, discussed the CEPHEUS, IMROZ, and BENEFIT trials of treatment for transplant-ineligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
Read More
Key Trials From ASH 2024 Impact Treatment for Plasma Cell Disorders Going Forward
February 20th 2025Peers & Perspectives in Oncology editorial board member Marc J. Braunstein, MD, PhD, FACP, discussed the significant advancements in multiple myeloma treatment at the 2024 ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Read More