High Predictive Value Is Observed for Circulating Tumor Tissue in Oropharyngeal Cancer
Results from a study evaluating circulating tumor tissue–modified viral (TTMV)–human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA among patients treated for HPV-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma is of interest.
The ability to predict disease recurrence is a clinically useful tool for any blood test. Results from a study evaluating circulating tumor tissue–modified viral (TTMV)–human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA among patients treated for HPV-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma is of interest, according to research presented at the 2022 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancers Symposium.
The test produced a high positive predictive value (PPV) of 95% for patients who received treatment for HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer and may detect recurrence earlier than imaging or other standard methods of recurrence monitoring (FIGURE).1
“While detection of tumor-specific DNA circulating in a patient’s bloodstream has shown potential as a powerful yet minimally invasive diagnostic tool for several cancers, this is the first study to demonstrate broad clinical utility and validity of the biomarker in HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer,” Glenn J. Hanna, MD, director of the Center for Salivary and Rare Head and Neck Cancers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, said in his presentation of the data.
The primary aim of the multi-institutional study is to determine the PPV of circulating TTMV-HPV DNA to determine recurrent HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer during the surveillance period for patients.
The population of patients consisted of those treated for HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer without distant disease who were at least 3 months post completion of standard defi nitive therapy. HPV status was provided by the clinician, and patients also needed at least 1 TTMVHPV DNA result found during surveillance.
The investigators compared all positive results from the study to clinical disease status reported by the provider for confi rmation.
A total of 1076 test results were included in the research across 118 clinical sites. Investigators reported a median of 2 cases per site. The median age for the population was 63 years, and most patients were male (88%), had positive p16 status (99%), and had at least 1 TTMV-HPV DNA test result (78%). Twenty-two percent of the population had more than 1 test result. The median follow-up was 9 months (range, 6-22).
A total of 996 tests (92.6%) were negative, and the remaining 80 (7.4%) were positive. When evaluating those who were positive, 26% had known or confirmed disease and 74% had clinically indeterminate/no evidence of disease (NED) status.
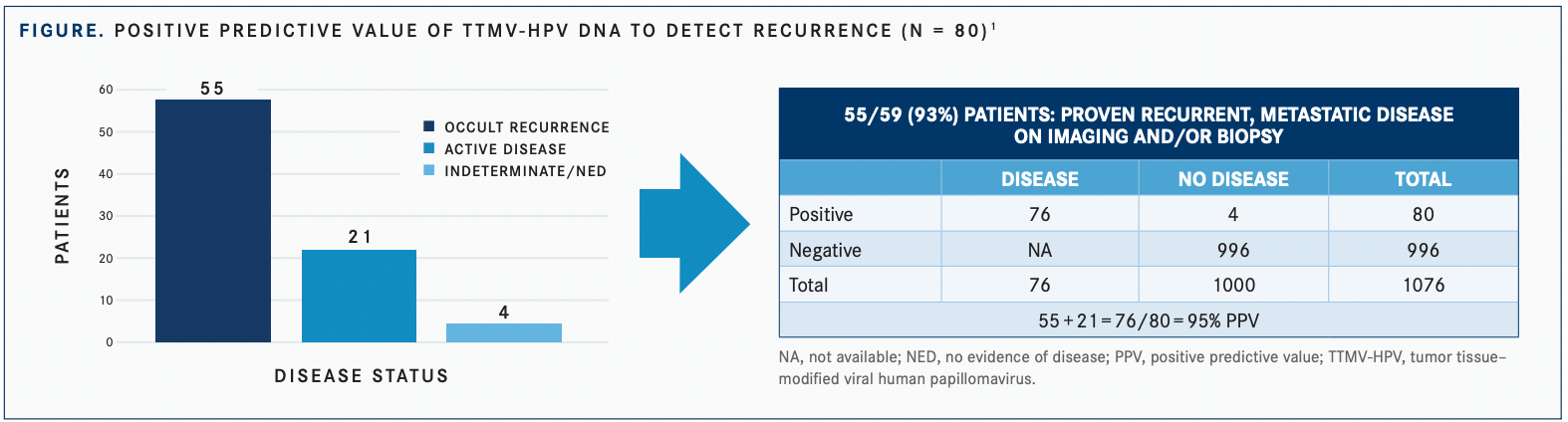
HPV-16 disease was eventually identified in 55 (93%) of 59 patients with a positive TTMV-HPV DNA test result. Of the 4 remaining patients, 2 had clinically suspicious lesions and 2 remained clinically NED; all 4 patients had TTMV-HPV DNA values between 16 and 79 fragments/mL. Moreover, 48% of patients with positive results and 46% with indeterminate/NED status were tested more than 12 months after treatment completion.
The values between patients with active disease and those with indeterminate/NED status were relatively similar and not statistically signifi cant, although a trend existed toward higher values in patients with active disease (P = .27).
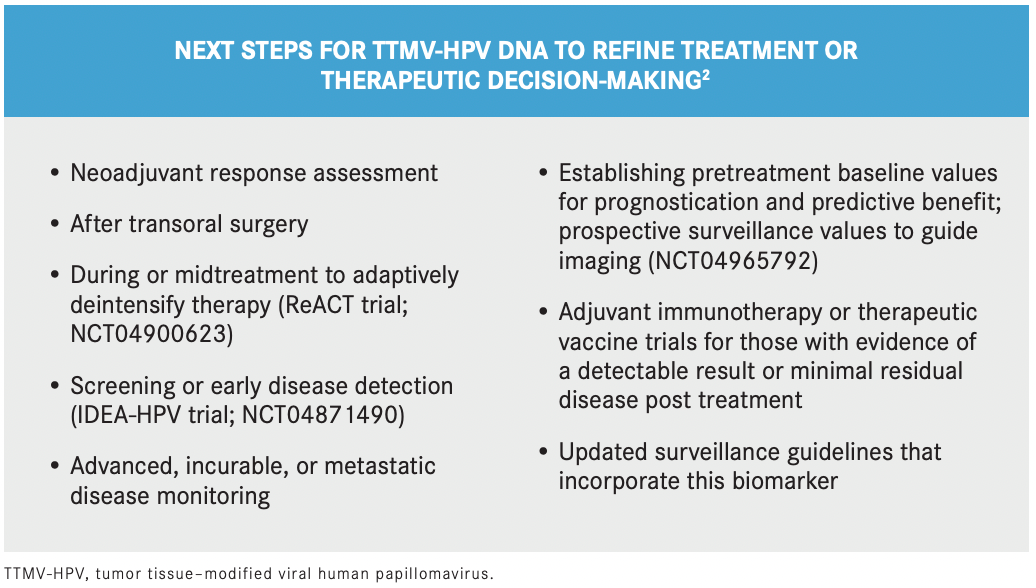
Hanna noted that establishing a cutoff value for determining clinically detectable disease is not feasible at this moment and that newly positive test results found during surveillance should prompt further examination to identify recurrence early. (See BOX2 for next steps for the use of TTMV-HPV DNA.)
“Most patients had no other evidence of disease or clinically indeterminate disease status at the time of their fi rst positive biomarker test,” he said. “Incorporating a test for TTMV-HPV DNA into routine posttreatment follow-up can enable physicians to detect recurrent cancers earlier and allow us to start recommended interventions more quickly to improve outcomes.”
REFERENCES
1. Berger BM, Hanna GJ, Genden E, et al. Detection of occult recurrence using circulating HPV tumor DNA among patients treated for HPV-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Presented at: 2022 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancers Symposium; February 24-26, 2022; Phoenix, AZ. Accessed February 24, 2022. https://bit. ly/3BUCTyn
2. Ward MC, Miller JA, Walker GV, Moeller BJ, Koyfman SA, Shah C. The economic impact of circulating tumor-tissue modifi ed HPV DNA for the post-treatment surveillance of HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer: a simulation. Oral Oncol. 2022;126:105721. doi:10.1016/j. oraloncology.2022.105721
Survivorship Care Promotes Evidence-Based Approaches for Quality of Life and Beyond
March 21st 2025Frank J. Penedo, PhD, explains the challenges of survivorship care for patients with cancer and how he implements programs to support patients’ emotional, physical, and practical needs.
Read More