Targeting the MET Pathway for Lung Cancer Treatments, Biomarkers
The MET oncogene has become a rapidly rising target for the treatment of patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to Balazs Halmos, MD, MS.
Balazs Halmos, MD, MS
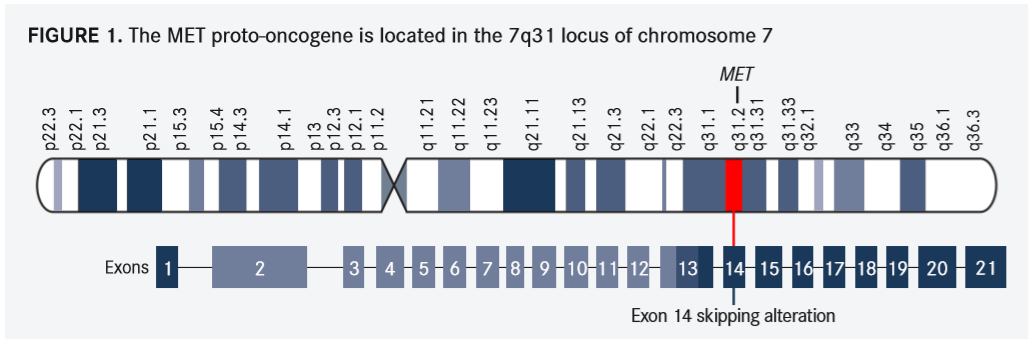
The MET oncogene has become a rapidly rising target for the treatment of patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to Balazs Halmos, MD, MS. Over the past several years, interest in MET has grown as investigators have considered it both as a biomarker and target for treatment, particularly with the targeting of MET exon 14 skipping mutations (FIGURE 1), leading to the development of several second-generation MET inhibitors.
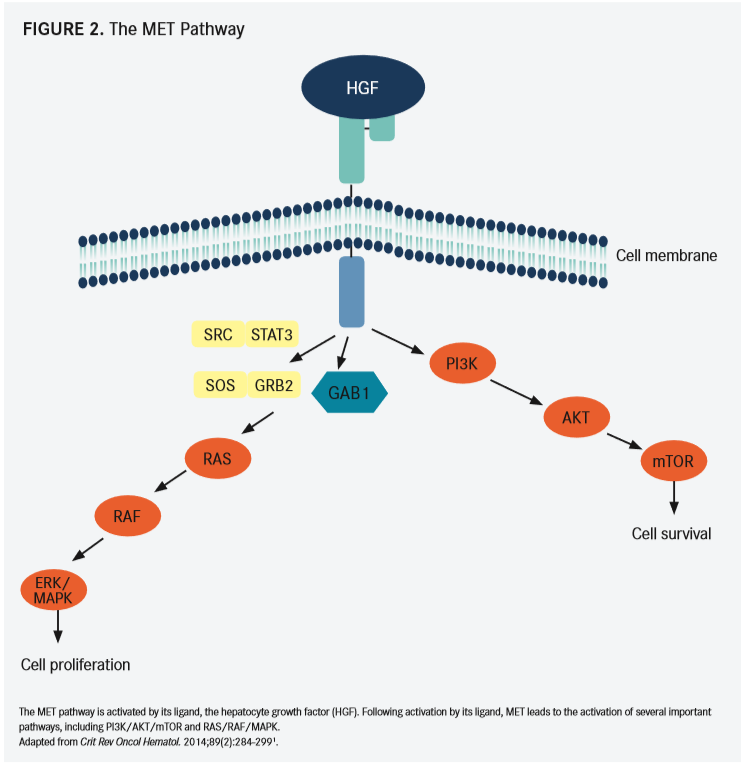
MET is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase, and this pathway (FIGURE 2) can be activated in one of several ways,1 explained Halmos, director of thoracic oncology, and director of clinical cancer genomics, Montefiore Medical Center, during a presentation at the12th AnnualNew York Lung Cancers Symposium, hosted by Physicians’ Education Resource®, LLC. The pathway can be activated through protein overexpression; increased expression of its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor;METmutations; gene amplification; and alternative splicing or exon 14 skipping. Each of these methods has been investigated as a potential approach to utilize this pathway for the treatment of patients with cancer.
“This plethora of possibilities led to a lot of confusion in the field over the years over which biomarker to use for selecting patients for MET-targeted therapy,” Halmos said.
Using MET protein overexpression as a biomarker led to the failure of several randomized studies. For example, the phase III METLung trial of onartuzumab (MetMAb) in combination with erlotinib (Tarceva) failed to meet its primary endpoint of improved overall survival (OS) with added onartuzumab in patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Onartuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the extracellular domain of MET, yet the combination regimen with onartuzumab demonstrated a median OS of 6.8 months compared with 9.1 months for erlotinib and placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 1.27; 95% CI, 0.98-1.65;P= .067).2The investigators noted that there may be better ways to select patients for MET-targeted therapy than with MET immunohistochemistry.
A greater signal for MET as an actionable target was seen with the use ofMETamplification. In the PROFILE 001 study, crizotinib (Xalkori) was investigated in patients with c-METamplified, advanced NSCLC. Although crizotinib is often used in patients withALK- orROS1-rearranged lung cancers, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) was originally developed as a type Ia MET inhibitor, Halmos noted. The small trial showed several responses to crizotinib, especially among patients with a higherMET-to-chromosome 7 centromere (MET/CEP7) ratio of ≥5.3
“In patients with a very high copy number of MET, suddenly there’s a lack of other critical driver oncogenes being presented;[this] suggested that in those cancers,METamplification can be the sole clinical driver,” Halmos said. However, he noted that it was difficult for investigators to find the rightMET/CEP7 threshold for identifying patients for such MET-targeted treatment. Although the threshold changes from study to study, the minimum has been set at 5 for highMETamplification.
Use of MET inhibition has also been investigated in combinations as a method of bypassing resistance to treatments. The overall frequency ofMET-driven acquired resistance is likely to be about 2% to 5%, Halmos said.
“It seems that the overexpressed MET kinase clusters on the cell surface along with EGFR, and basically creates a complex on the cell surface that leads to an unconventional EGFR signaling not requiring the ATP binding activity of EGFR. As a result, EGFR inhibition on its own is not successful and dual inhibition is necessary.”
An ongoing phase Ib study of savolitinib, a type Ib MET inhibitor, in combination with gefitinib (Iressa) in patients withEGFR-mutated, c-METpositive NSCLC who had acquired resistance to a prior EGFR TKI, has demonstrated clinical activity for the combination of dual MET and EGFR inhibition in resistant patients. As of data cutoff, the overall response rate (ORR) was 31%. Interestingly, the ORR was 52% in T790M-negative patients and 9% in T790M- positive patients.4
TARGETING MET EXON 14 SKIPPING MUTATIONS
Although a number of mutations of theMETgene can be identified, investigators have found that in patients with NSCLC, most cluster around exon 14 (FIGURE 1), Halmos said.
“WhenMETexon 14 is skipped…a very specific piece of the MET protein will be missing, and this particular piece contains a critical tyrosine residue. This tyrosine residue is important for CBL binding leading to the degradation of MET,” he explained. Without the tyrosine residue, MET is not degraded appropriately and can remain overactivated and oncogenic.
Overall, this mutation is found in approximately 3% of patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and in 22% of patients with sarcomatoid carcinoma. Among the patients with nonsquamous NSCLC and aMETexon 14 skipping mutation, 68% had an adenocarcinoma histology. Additionally, there tended to be an overlap betweenMETexon 14 skipping alterations andMETamplification in patients with advanced lung cancer.5
“The presence of this specific mutation also marks these cancer cells for great sensitivity against MET-targeted compounds, such as crizotinib, cabozantinib [Cabometyx], and a number of new molecules that are being developed,” Halmos said in an interview withTargeted Therapies in Oncology™. “So, finding patients with theseMETexon 14 mutations is critical because they can do just as well with the targeted treatment asALK-,ROS-, andEGFR-mutated patients.”
In a retrospective study of patients with aMETexon 14 skipping mutation treated with a MET inhibitor, the median OS was 24.6 months compared with 8.1 months in patients who did not receive MET-targeted therapy (HR, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01-0.92;P= .04). Crizotinib was given to 22 patients who experienced a median progression-free survival of 7.36 months.6Halmos noted, however, that there was some survivor bias in this study.
METexon 14−altered cancers can also express high levels of PD-L1, yet this does not translate into significant clinical benefit with immunotherapies, Halmos said. In a study of patients with recurrent or metastatic NSCLC who harbored aMETexon 14 skipping mutation and who were being treated with checkpoint inhibitors, the ORR from all 63 patients included in the study was 13%. In patients with PD-L1 expression ≥50%, the ORR was 33%, and in patients with no PD-L1 expression, the ORR was 20%.7
“[This] reaffirms that molecular testing doesn’t just help us identify patients for molecular treatment, it helps us understand immunotherapy, as well, outside of tumor mutation burden. So, we need to get this multigene testing for all of our patients if we want to continue to advance the care of our patients,” Halmos said during his presentation.
Interest in the treatment of patients withMETexon skipping mutations with MET inhibitors has led to the development of newer MET inhibitors, such as capmatinib, tepotinib, and glesatinib, with several others in preclinical stages.
References
- Gelsomino F, Facchinetti F, Haspinger ER, et al. Targeting the MET gene for the treatment of non-smallcell lung cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;89(2):284-299. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.11.006.
- Spigel DR, Edelman MJ, O’Byrne K, et al. Results from the phase III randomized trial of onartuzumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib in previously treated stage IIIB or IV non-small-cell lung cancer: METLung.J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(4):412-420. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.2160.
- Camidge DR, Ou SHI, Shapiro G, et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients with advanced c-MET-amplified non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(suppl 5s; abstr 8001). meetinglibrary.asco.org/record/92507/abstract.
- Yang JJ, Fang J, Shu Y, et al. A phase Ib trial of savolitinib plus gefitinib for Chinese patients with EGFR-mutant MET-amplified advanced NSCLC. Presented at: 2017 International Associatio for the Study of Lung Cancer World Conference on Lung Cancer; October 15-18, 2017; Yokohama, Japan. Abstract OA 09.06. library.iaslc.org/search-speaker?search_speaker=55340.
- Awad MM, Oxnard GR, Jackman DM, et al. MET exon 14 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer are associated with advanced age and stage-dependent MET genomic amplification and c-met overexpression.J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(7):721-730. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.4600.
- Awad MM, Leonardi GC, Kravets S, et al. Impact of MET inhibitors on survival among patients (pts) with MET exon 14 mutant (METdel14) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Clin Oncol.2017;35(suppl; abstr 8511). meetinglibrary.asco.org/record/145462/abstract.
- Sabari JK, Montecalvo J, Chen R, et al. PD-L1 expression and response to immunotherapy in patients with MET exon 14-altered non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC).J Clin Oncol.2017;35(suppl; abstr 8512). meetinglibrary.asco.org/record/152528/abstract.
Kim Evaluates New Regimens for EGFR+ Lung Cancer
January 20th 2025During a Community Case Forum event in partnership with the Medical Oncology Association of Southern California, Edward S. Kim, MD, MBA, discussed the FLAURA2 and MARIPOSA trials of newer regimens for EGFR-positive lung cancer.
Read More
Roundtable Roundup: Lung Cancer Molecular Testing and ALK-Targeted Treatment
January 18th 2025In separate, live virtual events, Vincent K. Lam, MD, and Chul Kim, MD, MPH, discuss molecular assays and treatment options for a patient with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with participants.
Read More
Conservative Management Is on the Rise in Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer
January 17th 2025In an interview with Peers & Perspectives in Oncology, Michael S. Leapman, MD, MHS, discusses the significance of a 10-year rise in active surveillance and watchful waiting in patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer.
Read More
What Is Dark Zone Lymphoma, and Is It Clinically Relevant?
January 16th 2025Dark zone lymphoma includes aggressive B-cell lymphomas with shared molecular features. While some respond to escalated treatment, others remain resistant, highlighting the need for targeted approaches to improve outcomes.
Read More
